Wednesday, March 11, 2015
Friday, February 27, 2015
Sunday, January 4, 2015
Mycobacteriology Review Questions
1. A 18 year old foreign exchange student has a positive tuberculin (PPD) skin test. He had received a BCG vaccination as a child. A whole cell mitogen assay for M. tuberculosis was performed and was reported negative. This indicates which of the following:
a. He has active tuberculosis
b. He most likely has a non-tuberculosis mycobacteria infection
c. He has a positive skin test most likely due to his BCG vaccine
d. The whole cell mitogen assay is falsely negative
e. Both tests should be repeated because they should always agree in reactivity
2. Concentration and decontamination of respiratory specimens is necessary for processing of mycobacteria cultures. Which of the following is not a correct statement?
a. 4% NaOH is a common treatment used to decontaminate specimens
b. Oxalic acid is commonly used to decontaminate specimens that may contain a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
c. The speed of centrifugation is an important step for determining the sensitivity of stains and culture
d. One concentrated sputum specimen is all that is necessary for ruling out tuberculosis
e. Decontamination of respiratory specimens is based on raising the pH of the specimen to kill off contaminating bacteria
3. A 62 year old homeless man began coughing up sputum streaked with blood. Concentrated AFB stains revealed the presence of numerous Acid Fast Bacilli, moderate length and sticking together. Which is the correct statement:
a. The morphology of the organism in the AFB smear is consistent with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
b. A real time PCR assay could be performed on the expectorated sputum specimen to assist in confirming a diagnosis of M. tuberculosis
c. The sticking together of the organisms is consistent with M. tuberculosis producing cord factor
d. The PPD and whole cell mitogen assay on this patient should both be positive
e. All of the above
4. A 40 year old male with HIV/AIDS develops a gradual onset of fatigue and anorexia. The causative organism grew in AFB culture after 14 days, smooth colony, with an AFB stain positive for bacilli variable in size, but mostly small rods. The AFB in culture was a non-photochromogen, biochemically inert, making molecular identification necessary. The most likely organism causing this infection is:
a. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
b. Mycobacterium avium-intracelullare complex
c. Mycobacterium fortuitum
d. Mycobacterium kansasii
e. Mycobacterium marinum
5. A 60 year old male with chronic pulmonary disease develops a cough with the production of a small amount of blood tinged sputum. An expectorated sputum specimen was collected. The specimen grew from AFB culture a photochromagen, Niacin negative, Nitrate positive, 68 *C catalase positive, and the organisms in the AFB stain were in the shape of a Shepherd’s crook. The organism is most likely:
a. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
b. Mycobacterium xenopi
c. Mycobacterium scrofulaceum
d. Mycobacterium kansasii
e. Mycobacterium szulgai
6. A 30 year old female developed a tender red subcutaneous nodule on her hand following the cleaning of a salt water fish tank. During the cleaning she scraped her hand on rocks in the bottom of the tank. A biopsy from the lesion was cultured. The organism did not grow at 37*C (8% CO2)but grew an AFB identified to be a photochromagen at 30*C (8% CO2) The organisms is most likely:
a. Mycobacterium ulcerans
b. Mycobacterium marinum
c. Mycobacterium kansasii
d. Mycobacterium fortuitum
e. Mycobacterium chelonae complex
7. A HIV/AIDS patient developed a cough and low-grade fever. A sputum specimen was cultured for AFB and grew an organism at 14 days from Lowenstein-Jensen (LJ) medium incubated at both 42*C and 35*C. (8% CO2). The colony appeared “egg nest” like on the LJ medium. The organism is identified as:
a. Mycobacterium szulgai
b. Mycobacterium chelonae
c. Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex
d. Mycobacterium xenopi
e. Mycobacterium kansasii
8. A 45 year old male with chronic lymphocytic leukemia develops painful nodular lesions on his chest. A biopsy of the nodules were submitted for AFB culture. There was no growth on Lowenstein-Jensen medium at 37*C or 30*C (8% CO2). The biopsy material grew when plated on a chocolate agar medium and incubated at 30*C (8% Co2) The organism is most likely:
a. Mycobacterium chelonae complex
b. Mycobacterium fortuitum
c. Mycobacerium abscessus
d. Mycobacerium hemophilum
e. Mycobacterium szulgai
9. A 70 year old male developed numbness of the left earlobe. A biopsy of the earlobe was submitted for AFB culture and submitted to anatomic pathology for staining. The AFB culture showed no growth after 8 weeks when cultured on appropriate media at both 37* and 30 *C (8% Co2). The Kinyoun/ZN type stain from tissue showed numerous AFB in a “school of fish” arrangement. What statement(s) is not true:
a. Mycobacterium leprae is the likely cause of this infection
b. Real time PCR on the biopsy tissue could help establish the diagnosis
c. Addition of hemin to the culture medium with help the organism grow
d. The animal reservoir for this organism is the armadillo
e. All of the above
10. A 10 year old female developed a draining cervical lymph node. The lymph node was biopsied and an AFB culture was submitted. An AFB grew after 14 days on Lowenstein-Jensen medium at 37*C (8% CO2). The colony was described as buff in color and cauliflower morphology. Biochemical reactions include Niacin positive and Nitrate positive. This infection is caused by:
a. Mycobacterium scrofulaceum
b. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
c. Mycobacterium abscessus
d. Mycobacterium chelonae complex
e. Mycobacterium avium-intraceullare complex
Key:
1. C2. D
3. E
4. B
5. D
6. B
7. D
8. D
9. C
10. B
Mycology Review Questions
1. A 40 year-old man presents to his physician with a 4 day history of terrible headache, fever, confusion, and staggering gait. His HIV status is unknown. A lumbar puncture is performed and CSF is sent to the laboratory. Which of the following results would you expect from this patient’s CSF studies:
a. Normal CSF pressure with a high protein level
b. India ink test with presence of encapsulated yeast
c. Elevated polymorphonuclear cells with high protein levels
d. Positive Galactomannan assay
e. Positive Ouchterlony-mannan test for Candida species
2. A yeast is identified in the laboratory with the following features; chlamydospore production, germ tube production and green pigment produced on ChromAgar. The yeast is identified as:
a. Candida dublinensis
b. Candida tropicalis
c. Candida glabrata
d. Candida albicans
e. Candida lusitaniae
3. A 32 year-old female presents to her physician with a hypo-pigmented skin lesion. A skin scraping was submitted to the laboratory for KOH preparation and fungal culture. The KOH examination was described as hyphae with yeast like structures in a spaghetti and meatball arrangement. The yeast did not grow on Sabouraud’s agar after 72 hours of incubation. This infection is most likely due to:
a. Candida albicans
b. Malassezia furfur
c. Trichophyton rubrum
d. Microsporum canis
e. Prototheca species
4. A 27 year-old man from Missouri presents to his physician with shortness of breath, fever and fatigue. In addition to his job as an accountant, he enjoyed spelunking and trout fishing thorough out the year. A sputum was submitted for fungal culture and a white mold grew after 14 days of incubation at 30*C. Under the microscope the mold appeared as septate thin hyphae with both microconidia and large tuberculate macroconidia. The mold is identified as:
a. Coccidioides immitis
b. Blastomyces dermatitidis
c. Histoplasma capsulatum
d. Fusarium species
e. Sporothrix schenckii
5. This organism was isolated from the sputum of a 45 year-old female bone marrow transplant patient. The photograph was taken from an organism grown on inhibitory mold agar at 30*C after 7 days of incubation. The identification is:
a. Fusarium species
b. Penicillium species
c. Acremonium species
d. Scopulariopsis species
e. Paecilomyces species
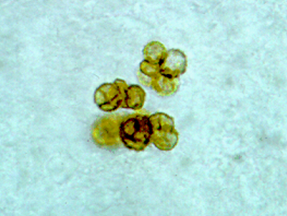
6. A 50 year-old male from Guatemala presented to his physician with a chronic skin lesion which overtime developed a cauliflower-like appearance. A biopsy was submitted for examination and revealed the structure seen in this photo. This structure is associated with what type of infection:
a. Phaeohyphomycoses
b. Chromoblastomycoses
c. Mycetoma
d. Sporotrichosis
e. Actinomycosis
7. A biopsy of an infected lung from a 50 year-old lung transplant patient revealed uniform hyphae with regularly spaced septation and branching at a 45 degree angle. No yeast cells were observed. Which of the following is the most probable diagnosis?
a. Actinomycosis
b. Aspergillosis
c. Blastomycosis
d. Cryptococcosis
e. Zygomycosis
8. A 56 year-old female complains of red nodular and ulcerative painful lesions on the right arm. She recalls being stuck with thorns while gardening. Her physician diagnosed a fungal infection. Which organisms is most likely the etiology?
a. Aspergillus fumigatus
b. Candida albicans
c. Nocardia asteroides
d. Sporothrix schenckii
e. Prototheca species
9. A 43 year-old female experienced fever and shortness of breath. She lived in the northwestern part of the US and spent time trekking through the forested areas of the region. Her sputum culture grew yeast on Sabouraud’s agar 8 – 10um in size, growth turned brown on birdseed agar, and blue on L-canavanine glycine brom-thymol blue medium.
a. Cryptococcus neoformans
b. Candida albicans
c. Cryptococcus gattii
d. Cryptococcus albidus
e. Candida dublinensis
10. A 45 year-old male complained of blockage of his nasal cavity by a slow growing lesion. He was a recent imigrant from Brazil. A biopsy of the lesion showed a large yeast cell with multiple buds appearing in a “mariners-wheel” type arrangement. Which organisms is the most likely etiology?
a. Blastomyces dermatitidis
b. Paracoccidioides brasileinsis
c. Prototheca species
d. Trichosporon beigelii
e. Cryptococcus albidus
Friday, December 19, 2014
More Questions - Somewhat Rarely Isolated Organisms
1. A 10 year-old boy spent the summer with his uncle in Mexico who lives on a dairy farm. He is complains of fever, hip pain and fatigue. He drank unpasteurized cow milk. The most likely organism causing his infection:
a. Francisella tularensis
b. Brucella abortus
c. Brucella melitensis
d. Bacillus cereus
e. Pasteurella multocida
2. Blood cultures were collected from the patient in Question #1. What would be expected to grow from this culture:
a. Small gram negative rod which took 5 days to grow in aerobic blood culture bottle
b. Large gram negative rod that grew in 24 hours in anaerobe bottle
c. Small gram negative rod that grew only after addition of cysteine to the blood culture bottle
d. Sea gull shaped gram negative rod that grew in 3 days in the aerobic bottle
e. This organism will not grow in routine blood culture bottles
3. A culture is received in the microbiology laboratory from a patient who was bit by his dog. The cultured organism has the reactions: small gram negative rod, grey pinpoint colony pitting the agar surface, oxidase positive, catalase negative, bleach type odor. The organism is most likely:
a. Pasteurella multocida
b. Eikinella corrodens
c. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
d. Cardiobacterium hominis
e. Haemophilus parainfluenzae
4. Positive patient blood culture grow an organism gram stain shows a gram negative cocco-bacilli, beta hemolytic colony on blood agar plate after 72 hours of incubation at 35*C and growing best on plates incubated in 5% C02 atmosphere, oxidase positive, catalase negative:
a. Haemophilus parainfluenza
b. Actinobacillus actinomycomitans
c. Kingella kingae
d. Cardiobacterium hominis
e. Eikinella corodens
5. An organism isolated from a positive blood culture from a patient in the intensive care unit. The organism isolated grows well on a Blood agar plate incubated at 35*C in room air, grey non-hemolytic colony, gram positive rod (diphtheroid like), non-motile, catalase positive, urease negative, resistant to most antibiotics but susceptible to vancomycin.
a. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
b. Corynebacterium jeikeium
c. Listeria monocytogenes
d. Corynebacterium urealyticusm
e. Bacillus cereus
6. A positive blood culture at 36 hours grows an organism on Gram stain shows gram positive cocci in pairs and chains. Initial subculture onto Blood agar plate incubated at 35*C in 5% CO2 shows “no growth”. However, the organism has satellite growth as pinpoint colonies around a streak of Staphylococcus aureus on a blood agar plate. The organism is most consistent with:
a. Streptococcus anginosus
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Abiotrophia species
d. Gemella species
e. Rothia species
7. A positive blood culture is gram stained and shows a gram negative diplococcius, grows on Blood agar and Chocolate agar media incubated at 35 *C in 5% CO2., oxidase positive, utilize the carbohydrates glucose and maltose, but cannot utilize sucrose or lactose. This organism is most likely:
a. Neisseria lactamica
b. Kingella kingae
c. Neisseria meningitidis
d. Moraxella catarrhalis
e. Neisseria gonorrnoeae
8. A wound culture is submitted to microbiology which grows gram positive cocci in clusters, white non-hemolytic colony on blood agar plate, coagulase negative, catalase positive, PYR positive. Identification is most likely:
a. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
b. Staphylococcus haemolyticus
c. Enterococcus faecalis
d. Enterococcus faecium
e. Staphylococcus ludgeninsis
9. A positive blood culture is gram stained and shows a short gram positive rod, alpha hemolytic colony on blood agar plate, catalase negative, non-motile, non-spore producer, H2S produced on a triple sugar iron agar slant:
a. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
b. Listeria monocytogenes
c. Corynebacterium urealyticus
d. Corynebacterium jeikeium
e. Bacillus cereus
10. A culture was performed from a lymph node aspirate, gram stain shows a gram negative rod that has bipolar staining (like a safety pin), grows on a blood agar plate incubated at 35*C in 5% CO2, oxidase negative, catalase positive. The person had been on an extended hike in the Southwest and reported some insect bites.
a. Francisella tularensis
b. Cardiobacterium hominis
c. Yersinia pestis
d. Haemophilus parainfluenza
e. Brucella canis
Key: 1.B 2.A 3.B 4.C 5.B 6.C 7.C 8.E 9.A 10.C
Tuesday, December 16, 2014
Dr. Morgan’s Microbes Questions #2 – Antibacterial Agents
1. Antibiotic choice for pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila:
a. Penicillinb. Macrolide antibiotic/Erythromycin
c. Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
d. Imipenem
e. Vancomycin
2. Antibiotic choice for Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis:
a. Cefotaximeb. Erythromycin plus Gentamicin
c. Tetracycline
d. Ampicillin plus Gentamicin
e. Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
3. Antibiotic choice for complicated pneumonia caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae with a Penicillin MIC = 4 mcg/ml and susceptible to other antibiotics tested.
a. Penicillinb. Cefotaxime
c. Vancomycin
d. Imipenem
e. Ertapenem
4. Antibiotic choice for bacteremia caused by a Staphylococcus aureus strain detected to have a mecA gene:
a. Ampicillinb. Vancomycin
c. Cefotaxime
d. Cefazolin
e. Imipenem
5. Antibiotic choice for a urinary tract infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae detected to have carbapenamase enzyme:
a. Ampicillinb. Ceftriaxone
c. Gentamicin
d. Colistin
e. Imipenem
6. Antibiotic choice to treat bacteremia caused by Escherichia coli with a CTX-M type enzyme:
a. Imipenemb. Cefotaxime
c. Ampicillin
d. Cefazolin
e. Ceftriaxone
7. A Staphylococcus aureus isolate was determined to be “D” test positive – this eliminates the ability to use which antibiotic to treat a patient with soft tissue infection:
a. Ampicillinb. Vancomycin
c. Clindamycin
d. Erythromycin
e. Cefazolin
8. An immune suppressed cancer patient was diagnosed with Listeria monocytogenes bacteremia. The best choice for therapy would be:
a. Cefazolinb. Ampicillin
c. Gentamicin
d. Ceftriazone
e. Cefotazime
9. An elderly adult is diagnosed with Haemophilus influenza meningitis. The H. influenza is found to produce a beta-lactamase enzyme by the cefinase test. The positive reaction eliminates the ability to use which antibiotic:
a. Cefotaximeb. Ceftriaxone
c. Ampicillin
d. Vancomyin
e. Erythromycin
10. A 35 year old male was diagnosed with diarrhea caused by Shigella flexneri and required antibiotic therapy. The best choice for therapy would be:
a. Tetracyclineb. Ciprofloxacin
c. Erythromycin
d. Vancomycin
e. Clindamycin
Keys to the questions: 1.b 2.d 3.b 4.b 5.d 6.a 7.c 8.b 9.c 10.b
Monday, December 15, 2014
Dr. Morgan’s Microbes Questions – Short Case Histories
1. A 65 year old man is diagnosed with peritonitis due to a perforated colon. Anaerobic culture was performed with the following results: Gamma hemolytic gray colony on anaerobic blood agar, black pigmented colony on bile esculin agar, resistant to kanamycin, colistin and vancomycin. What is the most likely organism?
a. Escherichia coli
b. Bacteroides fragilis
c. Prevotella melaninogenica
d. Clostridium perfringens
e. Porphyromonas gingivalis
2. A 35 year old male visits the Emergency Department with problems breathing over 2 weeks after recovering from a bout of diarrhea and vomiting. Physical exam: ascending muscle weakness began with his toes. A stool culture from two weeks prior grew a small grey colony on Skirrow’s blood agar plate that Gram stained a “sea gull” shaped negative rod. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
a. Clostridium botulinum, botulism
b. Poliovirus, poliomyelitis
c. Campylobacter jejuni, Guillain-Barre syndrome
d. JC virus, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
3. A patient in the intensive care unit developed severe watery diarrhea and pseudomembranous colitis after 5 days of antibiotics. The disease occurred as a result of which of the following?
a. Lecithinase
b. Hyaluronidase
c. Shiga toxin
d. Collagenase
e. Toxins A and B
4. A patient in the intensive care unit grows Gram positive cocci in pairs and chains from a blood culture. The organism is PYR positive, bile esculin positive, and 6.5% salt tolerant. This organism is most likely:
a. Streptococcus pneumonia
b. Streptococcus pyogenes
c. Streptococcus bovis
d. Streptococcus anginosis group
e. Enterococcus faecium
5. An 85 year old female arrives in the Emergency Department and is diagnosed with bacterial meningitis. The Cerebrospinal fluid Gram stain has numerous PMNs and a Gram positive lancet shaped cocci in pairs and short chains. The organism is most likely:
a. Listeria monocytogenes
b. Viridans group Streptococcus
c. Streptococcus agalactiae
d. Streptococcus pneumonia
e. Streptococcus anginosis group
6. A 4 year old girl arrives at the Emergency Department in renal failure. She had bloody diarrhea and severe hematological abnormalities. She loved to eat chicken pieces, hamburgers and French fries from a local restaurant. The most likely organism to cause this disease is:
a. Salmonella typhi
b. Campylobacter jejuni
c. Yersinia enterocolitica
d. Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli
e. Vibrio vulnificus
7. A 50 year old male presents to his doctor with a history of vomiting blood. He is thought to have a peptic ulcer. He is sent for endoscopy to obtain an antral biopsy specimen. A rapid test is performed on the antral biopsy to diagnose the presence of Helicobacter pylori. This rapid test would most likely be:
a. Gram stain for curved Gram negative rods
b. Oxidase production
c. Catalase reaction
d. Urease production
e. Occult blood reaction
8. An elderly woman arrives in the Emergency Department with a headache, fever, and nuchal rigidity. The Gram stain of the CSF shows numerous polys and small gram negative rods. The organism did not grow on blood agar plate, but grew on chocolate agar when incubated in the Co2 incubator. The organism required X and V growth factors. This patient most likely has:
a. Eikinella corrodens
b. Haemophilus influenza
c. Haemophilus parainfluenza
d. Kingella kingae
e. Acinetobacter baumannii
9. A 45 year old homeless man arrives in the Emergency Department complaining of difficulty breathing and spitting up bloody sputum that could be described as “currant jelly” like. The organism most likely causing this infection is:
a. Escherichia coli
b. Klebsiella pneumonia
c. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d. Streptococcus pneumonia
e. Serratia marcescens
10. A pregnant female has flu-like illness with possible sepsis. Blood cultures are collected and become positive after 24 hours of incubation. The organism isolated from the blood culture is a Gram positive cocci to short rod which is catalase positive, bile esculin positive and exhibits tumbling motility. This organism is most likely:
a. Enterococcus faecalis
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Corynebacterium species
d. Listeria monogytogenes
e. Gemella species
----------------------------------------------------
Questions key:
1.b 2.c 3.e 4.e 5.d 6.b 7.d 8.b 9.b 10.d
---------------------------------------------------
Monday, December 1, 2014
Tuesday, September 2, 2014
Wednesday, May 14, 2014
Tuesday, January 21, 2014
Wednesday, November 20, 2013
Sunday, September 8, 2013
MYCOLOGY REVIEW
Just the basics – meant for board review or brief study of this fascinating area of microbiology!
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)